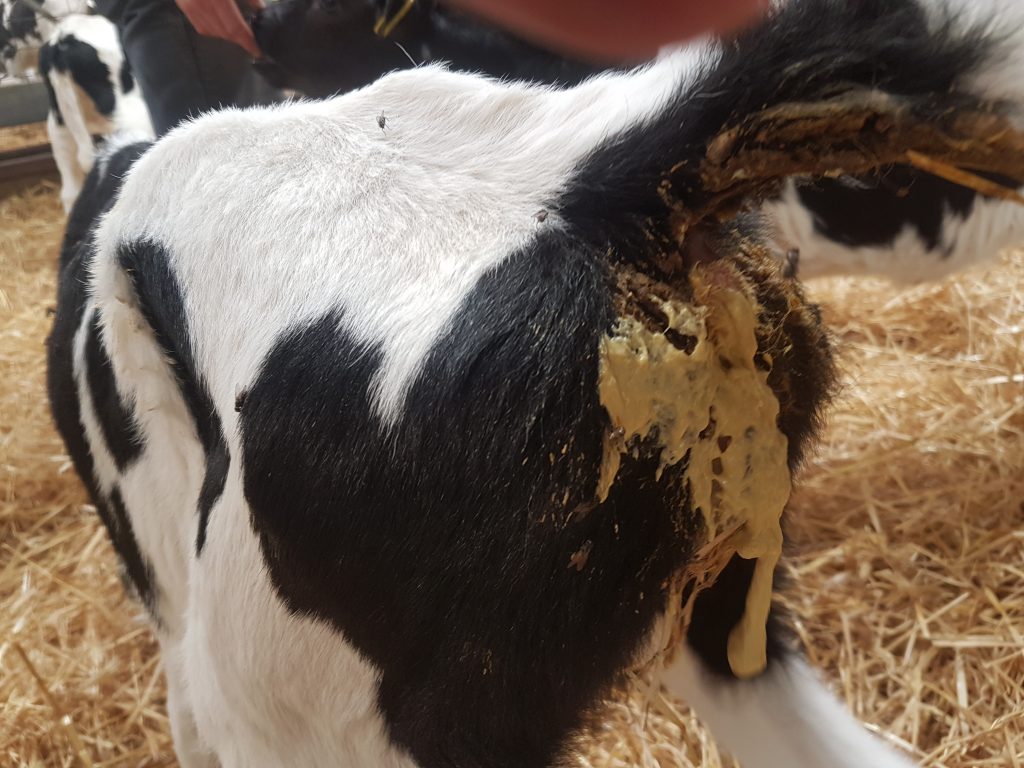
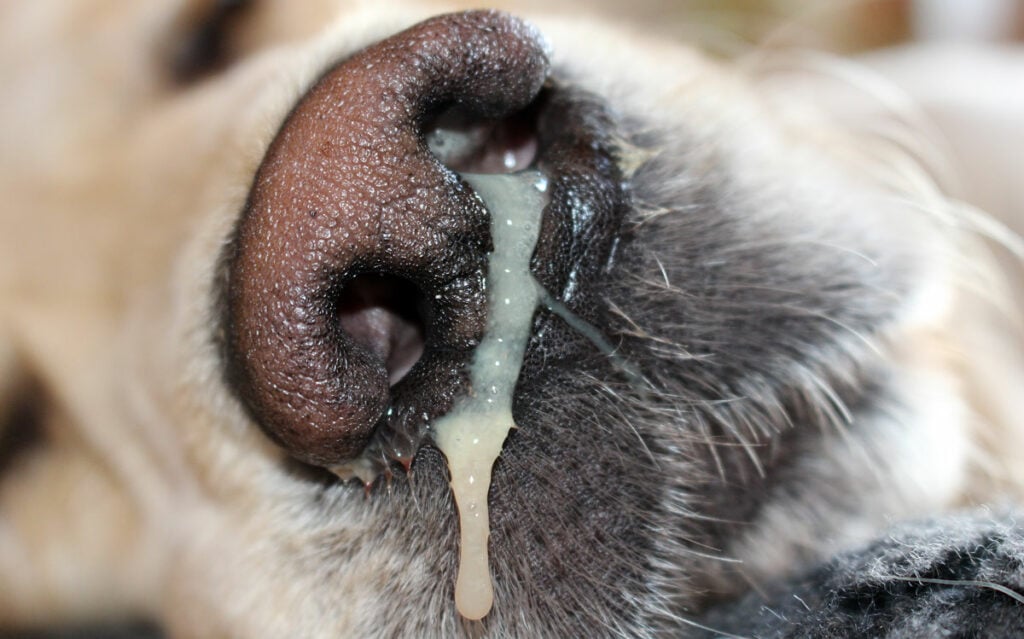
White scour, or neonatal diarrhea, is a diffuse and potentially fatal condition in selected groups, such as calves and yards. The aquatic dearest, white to pale yellow, marks this condition, possibly leading to dehydration and weight loss if not treated before. Familiarity with the causes, symptoms, and prevention of white frost is important for veterinarians, farmers, and pet owners.
What is White Scour?
White scour is a type of diarrhea that typically happens in newborn animals in the first days or weeks. Bear the white color name of excrement, which can vary from the blank to the cream or yellow depending on the cause. White scours is not a disease but a clinical symptom of some infection or issues that compromise the digestive system.
Causes of White Scour
White scour can be due to infectious and non-infectious causes:
1. Infectious Causes
- Escherichia coli (E. coli): A frequent bacterial pathogen causing scour in neonates. Enterotoxigenic E. coli secretes toxins that interfere with water absorption by the intestines.
- Rotavirus and Coronavirus: These viruses invade the intestinal lining, inhibiting nutrient absorption and causing diarrhea.
- Cryptosporidium spp: A protozoan parasite that causes damage to the intestine and watery diarrhea, resistant to most conventional therapies.
- Clostridium perfringens: Severe, in some cases bloody scourge, of bacterial origin, and usually rapid worsening.
2. Non-Infectious Causes
- Failure of passive transfer (FPT): A Newborn that is not well-nourished by high-quality colostrum in a short time becomes vulnerable to infection due to its weakened immune system.
- Bad hygiene and crowding: A Filthy environment that promotes close exposure to disease organisms.
- Cold stress and malnutrition: Stress from the environment and poor feeding can compromise the immune system, predisposing the animal.
Symptoms of White Scour
- White or light-colored, pale, watery diarrhea
- Dehydration (sunken eyes, tenting of the skin)
- Weakness and lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Cold extremities in advanced cases
If left untreated, white scours can lead to septicemia, hypoglycemia, and death.
Diagnosis
A veterinarian generally diagnoses white fraud on clinical grounds, it was to come and herbs of herbs. Laboratory tests, such as faecal samples and pathogenic identification, may be employed to ascertain the appropriate cause (eg, E. coli, rotavirus, cryptosporidium).
Treatment
The ultimate aims of treatment are to rehydrate, restore electrolyte balance, and treat the underlying cause.
1. Fluid Therapy
Oral rehydration solution (ORS) with electrolytes and glucose is the key in mild to moderate cases.
Severe attacks can be treated with intravenous fluids.
2. Antimicrobials
Employed when a bacterial infection is suspected or proven. However, not effective against viral or protozoal causes.
3. Supportive Care
Warmth: Keep the animal warm and dry to avoid hypothermia.
Nutrition: Maintain milk feeding alongside electrolytes, but keep the feeds apart by a few hours to prevent malabsorption of nutrients.
Prevention and Control
- Prevention is always better than a cure when it comes to white scours. The following are important strategies:
- Colostrum Management: Supply newborns with high-quality colostrum within the first 6 hours after birth.
- Hygiene: Use clean and dry bedding, equipment for feeding, and calving/lambing pens.
- Vaccination: Vaccinate breeding dams against routine scour pathogens such as E. coli and rotavirus to improve passive immunity.
- Proper Nutrition: Provide both the pregnant dam and newborn animal with a balanced diet after birth.
- Reduce Stress: Shield young stock from excessive cold and crowding.
Conclusion
The white Scour remains among the primary sources of neonatal loss in cattle. Anticipated detection, precise measurements, and control are crucial to curb their impact. The manufacturers require the assistance of veterinarians to institute the insurance and sales so that the risk of neonatal diarrhea can be minimized. Due to the optimal management and expected intervention methods, the devastating impact of the white scour can be lessened.